Lazy Loading
📌 지연 로딩(Lazy Loading)은 데이터를 실제로 사용할 때 데이터베이스에서 조회하는 방식
JPA의 지연로딩
- fetch 속성 사용
- FetchType.LAZY : 지연로딩
- 지연로딩을 사용하면 Proxy 객체를 조회한다.
- 연관된 객체(Company)를 매번 함께 조회하는것은 낭비인 경우에 사용한다.
@Entity
@Table(name = "tutor")
public class Tutor {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String name;
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY)
@JoinColumn(name = "company_id")
private Company company;
public Tutor() {
}
public Tutor(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public Company getCompany() {
return company;
}
public void setCompany(Company company) {
this.company = company;
}
}public class FetchTypeLazyMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EntityManagerFactory emf = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("entity");
EntityManager em = emf.createEntityManager();
EntityTransaction transaction = em.getTransaction();
transaction.begin();
try {
Company company = new Company("sparta");
em.persist(company);
Tutor tutor = new Tutor("wonuk");
tutor.setCompany(company);
em.persist(tutor);
// 영속성 컨텍스트 초기화
em.flush();
em.clear();
// em.find()
Tutor findTutor = em.find(Tutor.class, tutor.getId());
transaction.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
transaction.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
em.close();
}
emf.close();
}
}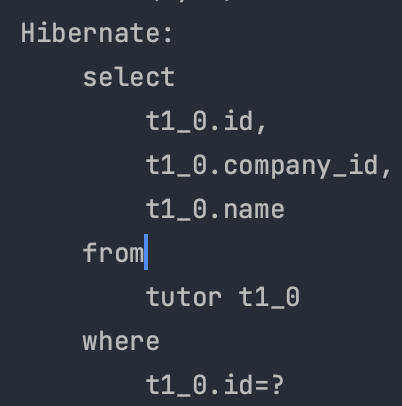
Tutor만 조회한다.
getCompany()
System.out.println("findTutor.getCompany().getClass() = " + findTutor.getCompany().getClass());
실행결과

Proxy로 조회한다.
getCompany().getName()
System.out.println("findTutor.getCompany().getName() = " + findTutor.getCompany().getName());
실행결과
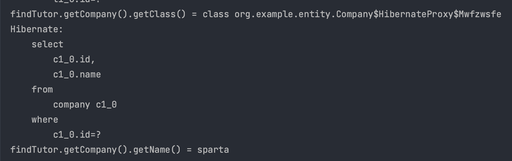
- 실제 값에 접근할 때 조회 SQL이 실행된다.
- 실제 Company 의 값을 사용하는 시점에 초기화(DB 조회)된다.
- 지연 로딩을 사용하면 연관된 객체를 Proxy로 조회한다.
Eager Loading
📌 즉시 로딩(Eager Loading)은 엔티티를 조회할 때 연관된 데이터까지 모두 한 번에 로드하는 방식
- JPA의 즉시 로딩
- fetch 속성 사용
- FetchType.EAGER : 즉시 로딩
- Proxy 객체를 조회하지 않고 한 번에 연관된 객체까지 조회한다.
- 연관된 객체(Company)를 매번 함께 조회하는것이 효율적인 경우에 사용한다.
- fetch 속성 사용
@Entity
@Table(name = "tutor")
public class Tutor {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String name;
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.EAGER)
@JoinColumn(name = "company_id")
private Company company;
public Tutor() {
}
public Tutor(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public Company getCompany() {
return company;
}
public void setCompany(Company company) {
this.company = company;
}
}public class FetchTypeEagerMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EntityManagerFactory emf = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("entity");
EntityManager em = emf.createEntityManager();
EntityTransaction transaction = em.getTransaction();
transaction.begin();
try {
Company company = new Company("sparta");
em.persist(company);
Tutor tutor = new Tutor("wonuk");
tutor.setCompany(company);
em.persist(tutor);
// 영속성 컨텍스트 초기화
em.flush();
em.clear();
// em.find()
Tutor findTutor = em.find(Tutor.class, tutor.getId());
// getCompany()
System.out.println("findTutor.getCompany().getClass() = " + findTutor.getCompany().getClass());
// getCompany().getName()
System.out.println("findTutor.getCompany().getName() = " + findTutor.getCompany().getName());
transaction.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
transaction.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
em.close();
}
emf.close();
}
}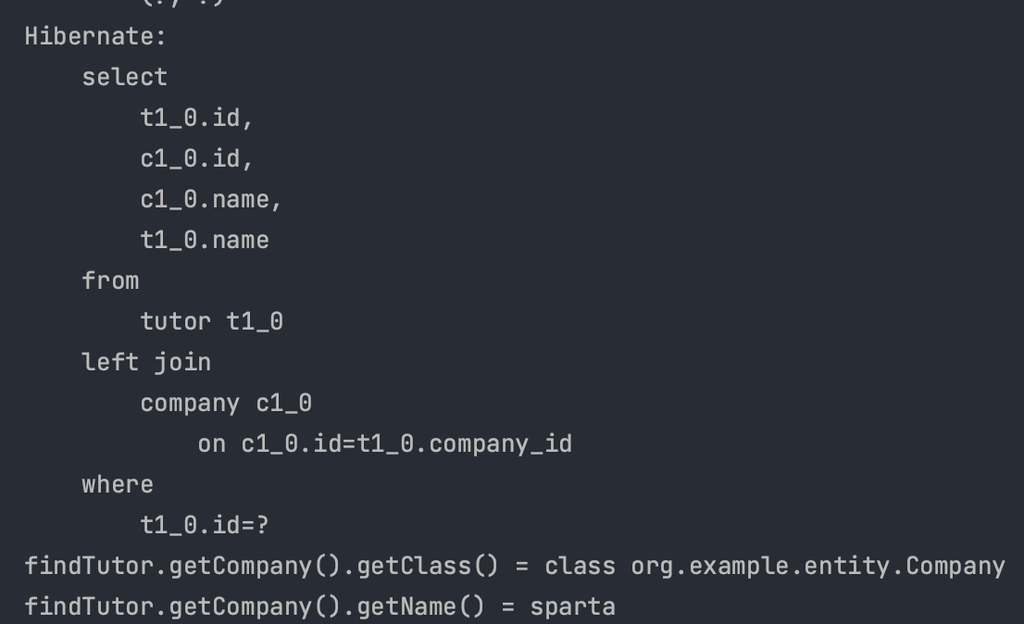
JOIN을 사용해 한번의 SQL로 모두 조회하기 때문에 Proxy가 필요없다.
즉시 로딩 주의점

코드 예시(N+1 문제)
List<Tutor> tutorList = em.createQuery("select t from Tutor t", Tutor.class).getResultList();
실행결과
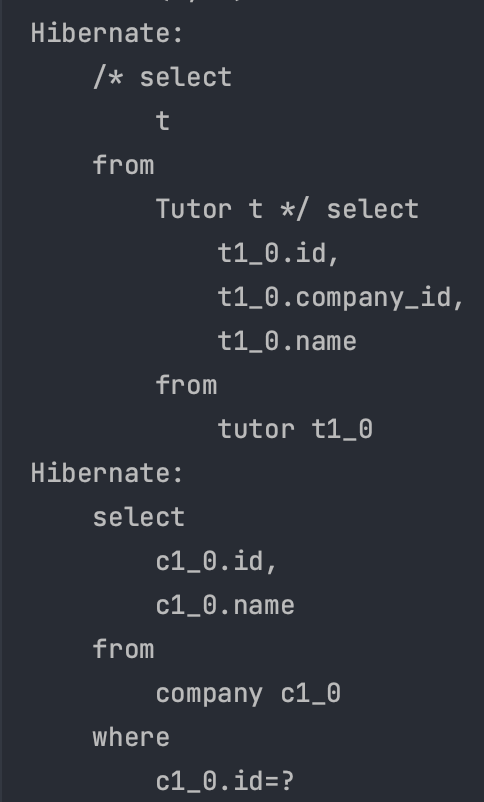
- 조회 SQL이 N+1번 실행된다.
- 처음 실행된 최초 SQL Query : 1(Tutor)
- 연관된 객체 조회 SQL Query : N(Company)
- JPQL은 SQL이 그대로 변환되어 조회된 Tutor 만큼 EAGER로 설정된 Company가 함께 조회된다.
- em.find() 는 JPA가 내부적으로 최적화한다.
N+1 문제 해결 방법
- 모든 연관관계를 LAZY로 설정한다.
- JPQL fetch join : Rumtime에 원하는 Entity를 함께 조회할 수 있다.(대부분 사용)
- @EntityGraph
- @BatchSize
- Native Query
'DB 접근 > JPA ( Java Persistence API )' 카테고리의 다른 글
| JPA와 Transaction (0) | 2025.01.17 |
|---|---|
| Proxy (0) | 2025.01.14 |
| 상속관계 매핑 (0) | 2025.01.13 |
| 연관관계 (0) | 2025.01.12 |
| [JPA] Spring Data JPA (0) | 2025.01.07 |